M270 PFAS Treatment for Sustainable Waste Management
M270 PFAS Treatment for Sustainable Waste Management
Blog Article
Advanced Approaches for Reliable PFAS Contamination Elimination
The relentless challenge of PFAS contamination requires the exploration of innovative removal approaches that can properly resolve these unsafe compounds. Cutting-edge innovations, such as advanced oxidation procedures and numerous adsorption strategies, have arised as promising remedies in mitigating PFAS from affected environments.
Understanding PFAS Features
Although per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds (PFAS) have been extensively utilized in different commercial and customer items as a result of their one-of-a-kind homes, their persistence in the setting positions considerable difficulties to public health and wellness and safety. PFAS are a team of synthetic chemicals characterized by a carbon-fluorine bond, among the greatest chemical bonds recognized, which adds to their phenomenal stability and resistance to degradation. This security allows PFAS to gather in the environment and living microorganisms, resulting in possible unfavorable wellness effects.
These same residential properties contribute to their environmental persistence, as PFAS do not easily break down through natural processes. Understanding the chemical properties of PFAS is essential for developing effective strategies to manage and minimize their ecological effect.
Ingenious Remediation Technologies
The persistence of PFAS in the setting has actually spurred the development of ingenious remediation innovations intended at effectively getting rid of these contaminants from influenced communities. Among one of the most promising methods are advanced oxidation procedures (AOPs), which make use of effective oxidants to damage down PFAS compounds into less hazardous substances. AOPs can be tailored to target particular PFAS structures, improving their efficacy.
An additional arising modern technology is the usage of adsorption media, such as turned on carbon and ion exchange resins, which can uniquely capture PFAS from infected water. These products have actually revealed significant removal efficiencies, although periodic substitute and regeneration are essential to preserve efficiency.
Membrane filtering techniques, consisting of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, are also obtaining grip in PFAS remediation. These techniques can efficiently divide PFAS from water, supplying a viable service for dealing with contaminated resources. In addition, thermal therapy techniques, such as incineration, can decay PFAS right into safe by-products, though they require cautious management to control emissions.
Jointly, these ingenious remediation innovations represent considerable innovations in the recurring fight against PFAS contamination, offering numerous strategies to restore affected environments and protect public health.

Bioremediation Methods
Bioremediation techniques supply a promising technique to dealing with PFAS contamination by harnessing the natural capabilities of microorganisms to degrade these relentless substances (m270 waste management). This approach involves making use of bacteria, fungis, and various other microbes that can metabolize or transform PFAS compounds right into much less damaging results
Current innovations in molecular biology and environmental microbiology have enhanced our understanding of microbial neighborhoods and their potential duties in PFAS deterioration. Researchers are proactively discovering details strains of microorganisms, such as Pseudomonas and Bacillus, which have shown the capacity to damage down certain PFAS compounds.
Sitting bioremediation techniques, where microbes are promoted straight in contaminated environments, can be particularly efficient. This technique often involves the application of nutrients or electron contributors to advertise microbial development and task. Additionally, ex situ techniques, such as bioreactors, enable for controlled problems that can optimize destruction prices.
Regardless of the pledge of bioremediation, obstacles stay, including the complex nature of PFAS compounds and the need for substantial area testing - m270 waste management. Continued r & d will be important to fine-tune these methods and analyze their effectiveness in diverse ecological contexts
Adsorption and Filtration Methods
Attending to PFAS m270 waste management contamination frequently involves using adsorption and filtration methods, which are made to get rid of these relentless chemicals from water and dirt. Amongst the different methods, triggered carbon adsorption is widely used as a result of its high surface area and porosity, enabling efficient capturing of PFAS particles. Granular turned on carbon (GAC) systems are particularly preferred for dealing with large quantities of polluted water, while powdered turned on carbon (PAC) can be utilized for smaller-scale applications.
Ion exchange materials likewise show promise in PFAS removal, working by trading PFAS ions with less hazardous ions in the water. This method has actually demonstrated performance in focusing PFAS substances, facilitating their subsequent removal. In addition, membrane layer filtration strategies, such as reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, run by making use of semi-permeable membrane layers to different PFAS from water, properly lowering their concentrations.
While these techniques are effective, they need to be thoroughly chosen based on the specific PFAS compounds present and the environmental context. Constant improvements in products science and engineering are resulting in the growth of novel adsorbents and filtering systems that enhance removal efficiencies and decrease operational expenses, thereby boosting general removal initiatives.
Regulatory and Plan Considerations
Just how can efficient regulative structures enhance the administration of PFAS contamination? Comprehensive plans are vital to make certain a worked with and robust reaction to the difficulties presented by per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds (PFAS) Laws can establish clear guidelines for monitoring, reporting, and remediating PFAS-contaminated sites, fostering accountability among sectors and public entities. (m270 waste management)
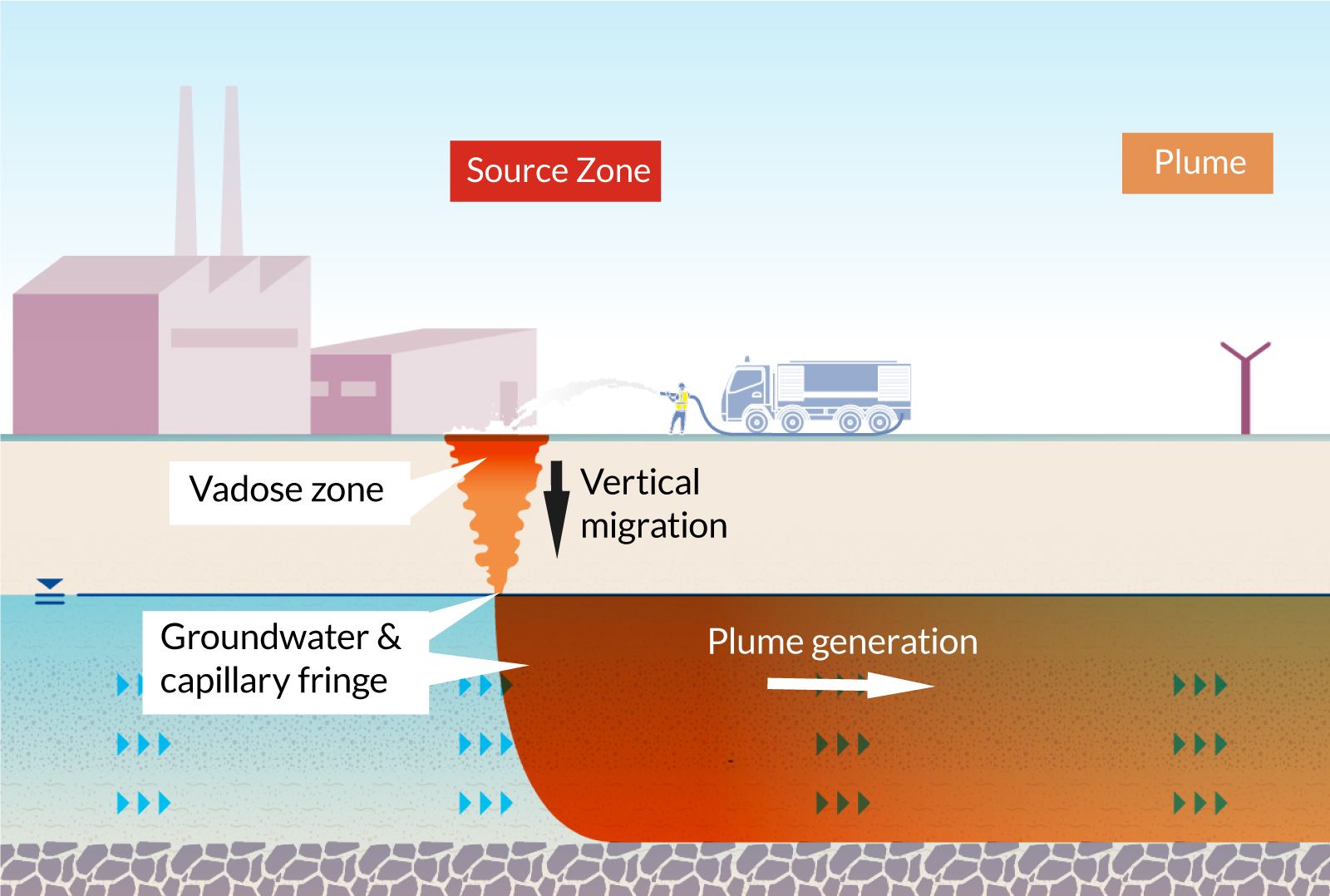
Additionally, financial motivations and gives can be integrated right into policies to motivate the fostering of advanced removal technologies. Policymakers need to also focus on r & d, ensuring that arising techniques for PFAS removal are verified and carried out properly.
In addition, public recognition and interaction are important parts of any kind of regulative method, empowering areas to support for their health and wellness. Inevitably, a well-structured regulatory setting will certainly not just boost the monitoring of PFAS contamination yet additionally promote sustainable methods that shield future generations.
Final Thought
In summary, the complexity of PFAS contamination necessitates the fostering of innovative remediation techniques. Cutting-edge technologies such as sophisticated oxidation procedures, adsorption strategies, and membrane filtration have actually shown significant efficiency in removing these persistent compounds from polluted water sources. Additionally, governing frameworks need to advance to support the execution of these modern technologies, ensuring risk-free and effective monitoring of PFAS contaminants. Continued r & d in this area continue to be essential to addressing the obstacles positioned by PFAS contamination.
Report this page